Graphics - Image Types and Size
Graphics are an integral part of presentations,
web pages, and computer programs. There are different types of graphics
that can be created, Bitmaps (or Raster) and Vectors. Graphics can
be obtained from a Digital Camera, the Web, Scanned images or you
can create them yourself in a photo editor program. It is important
to learn how to gain the smallest file size possible, while maintaining
image clarity to have graphics enhance your presentation or website.
Images
can be saved in various resolutions, which will affect the quality
of the image (sharpness/fuzziness), as well as how large the image
looks on the screen. The resolution will also affect the file size.
Bitmap vs. Vector
Bitmap
Bitmaps are digital images composed of dots or pixels. In a
bitmap image, the image file has to define the exact color of every
pixel in the image, therefore the more pixels which compose an image,
the larger its file size. The number of pixels in an image can be
increased in two ways; by making the image larger in a photo editor,
or by increasing the image resolution. One confusing thing about
the term bitmap is that there is a windows image format (.bmp) which
is also referred to as a 'bitmap'. To avoid this confusion,
some people use the term raster when referring to images composed
of pixels.
Vector
Vector images are not made up of dots, they are instead, composed
of shapes and lines. Vector shapes are defined by the direction
of the line which runs around the perimeter. Vectors has several
qualities; they are infinitely scaleable, they usually have smaller
file sizes than bitmaps and they are crisp and clear when printed.
Note: vectors on screen appear pixilated because the computer screen
is composed of pixels
When you increase
the size of a Bitmap, you can see all the pixilation, but when you
increase the size of a Vector, the edges remain smooth.
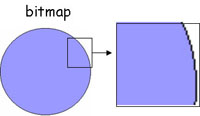
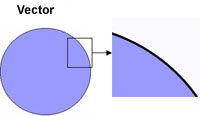
Bitmap Image
Types
There are many
different types of bitmap image files that are used, the most common
of which are JPEG, BMP, GIF, TIFF and PNG. Each has unique advantages
and disadvantages in terms of file size and image quality.
GIF
A GIF contains
a maximum of 256 distinct colors, that can be made transparent or
animated. When a GIF is altered information is not lost. GIF's are
excellent for images with large areas of flat colour, like clipart
or line-art, but are not recommended for photographs, or images with
many different colours.
Below you can
a good choice for GIF format, the clipart of the balloons, and a
bad choice for GIF format, the photograph of the tree.


JPG
JPG's Contains
up to 16 million distinct colors, excellent for photographs due
to its wide range of tones, but they can not be made transparent
or animated and are difficult to edit. JPG's have variable compression
levels and the image quality will degrade with each modification.
JPG is a popular format because it keeps photographic images clear
and it lets you adjust the amount of compression.
Below you will
find an example of a low resolution
JPG and a regular resolution JPG.


TIFF
TIFF's can go
through many modifications without losing any image quality, they
don't have a lossy compression. They are the best quality for digital
camera output but are not suitable for web pages .
BMP
BMP's are universally
supported but have large file sizes, which makes them not good for
webpages, even though they load quickly for viewing.
PNG
PNG's support
millions of colours and have a small file size. The image quality
will not degrade with many modifications but they are not supported
by older browsers and will eventually replace GIF image files.
File
Size
When posting pictures on your website
the general rule for file size is:
For a picture that will be about the size of an icon, 5-10 Kb
For a picture that will be about 1/4 of the page, 20-50 Kb
For a picture that will be about 800 X 600 pixels, 50-100 Kb
Home
| Image types
| Obtain Images
| Modify Images
| Photoshop
|